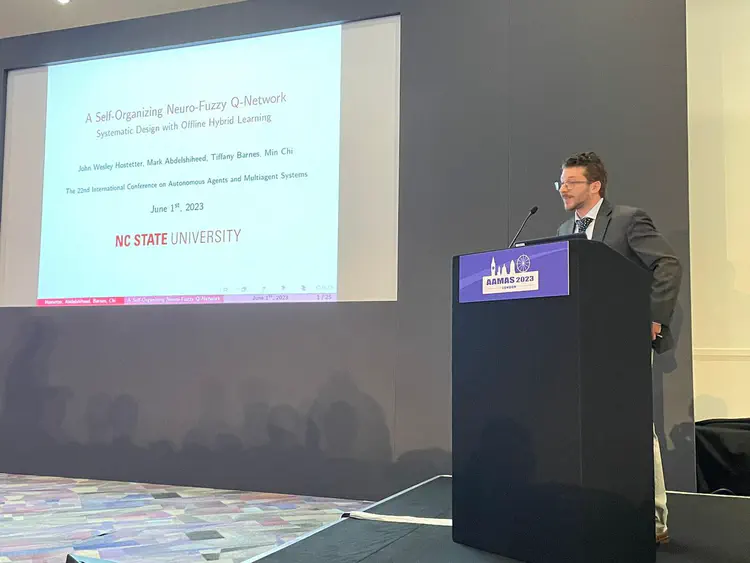
Introducing self-organizing neuro-fuzzy Q-networks
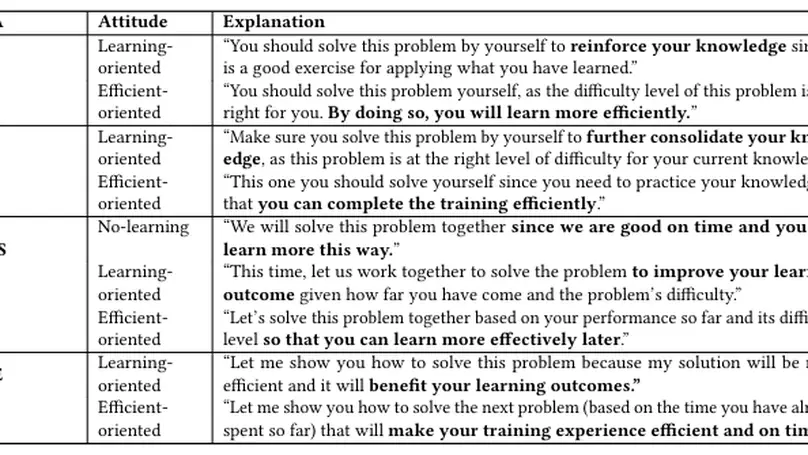
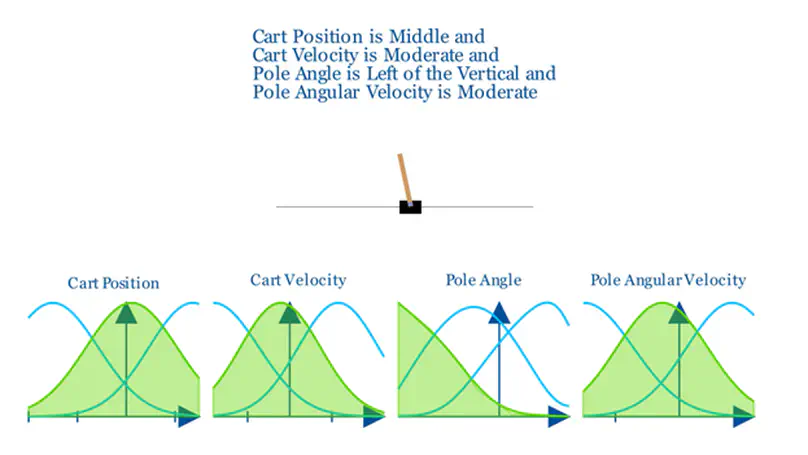
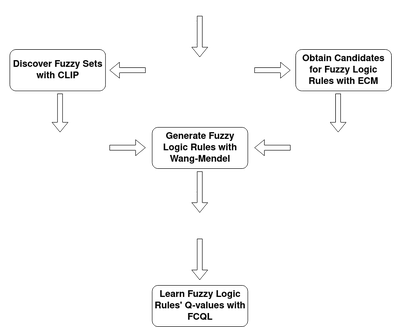
Trained with unsupervised learning and finished with an offline model-free fuzzy reinforcement learning approach called fuzzy conservative Q-learning (FCQL), this approach offers more effective and interpretable policies than deep neural networks, while facilitating human-in-the-loop design and explainability.
Code demonstrating our proposed method is publicly available.
John Wesley Hostetter
Assistant Professor of Analytics and Information Systems
Western Kentucky University
John Wesley Hostetter is an Assistant Professor of Analytics and Information Systems. His research interests are concerned with how a mathematical field studying impreciseness called fuzzy logic may aid in re-imagining function approximation in artificial intelligence. More specifically, he develops alternatives to artificial neural networks that are more interpretable called self-organizing neuro-fuzzy networks. These self-organizing neuro-fuzzy networks have the same power as artificial neural networks, but can explain their decision-making. Much of his published research leverages this novel and interpretable function approximation technique to improve undergraduate STEM education.
Skills
Fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, rough sets, approximate reasoning, impreciseness, vagueness, uncertainty
Supervised/unsupervised/reinforcement learning
Experience with PyTorch, Optuna, iGraph, etc.
Experience
Scholarships, Fellowships, Grants & Awards
Featured Publications
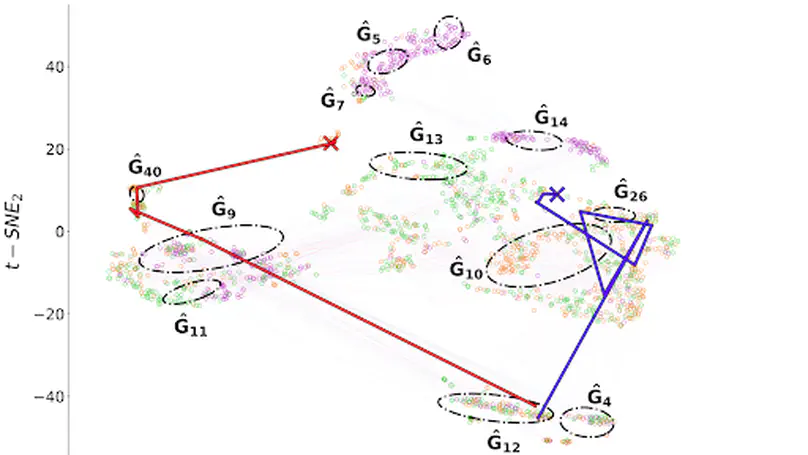
Neuro-fuzzy networks can be dramatically simplified using concepts from f-granulation and social network analysis.

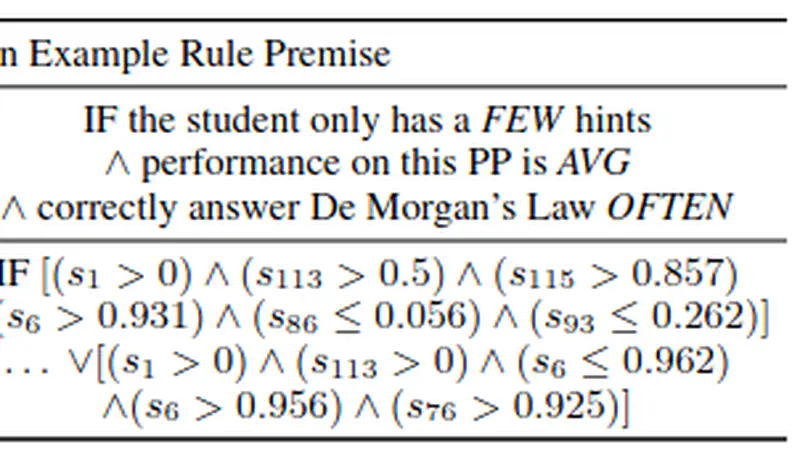
A simple and quick alternative to the famous Wang-Mendel Method for fuzzy logic rule generation is proposed and investigated; it is called the Latent Lockstep Method.